In the contemporary era, there is significant excitement surrounding green hydrogen and electrolyzers. Let’s delve deep into the concept further to understand what is an electrolyzer.
So, what is an Electrolyser? An electrolyser is an electrochemical device that utilizes electrical energy to drive a chemical reaction, in this case, the splitting of water molecules (H2O) into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) gases. Electrolyzers are a key technology to produce green hydrogen. Hydrogen produced through electrolysis, also known as “green hydrogen energy” is considered a clean and sustainable energy carrier.
The rate of growth in electrolysis capacity for the purpose of producing hydrogen has been slowing down in the last few years. In 2022, only around 130 MW of new capacity were put into operation, which is 45% less than the year before. But since last year, the capacity to produce electrolysers has grown by more than 25%, and by 2022, it is expected to reach over 11 GW annually.
With installed electrolysis capacity expected to reach more than 550 GW by 2030, the Net Zero Emissions by 2050 (NZE) scenario calls for a major acceleration of electrolysis capacity growth from a low base.
What Are The Different Types Of Electrolysers?
To understand the type of Electrolyser, we have to analyze the fact that there are different types of electrolysers.
Proton exchange membrane (PEM), alkaline, and solid oxide technologies are the three primary categories of water electrolysis technology. Each type of electrolysers functions slightly differently, depending on the electrolyte material involved.
Also Read: Blue Hydrogen and Green Hydrogen: A Comprehensive Overview
Alkaline Electrolysers:
Alkaline electrolysers contain water and a liquid electrolyte solution such as potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH). When current is applied to an alkaline cell stack, the hydroxide ions (OH) move through the electrolyte solutions from the cathode to the anode of each cell. The hydrogen gas bubbles are generated at the cathode, and the oxygen gas is generated at the anode.
Alkaline Electrolysers Uses:
1) Hydrogen Production:
Alkaline electrolysers are commonly used in large-scale industrial applications to produce hydrogen gas. This hydrogen can be used in a variety of industrial processes, such as petroleum refining and metal production.
2) Hydrogen Storage:
Alkaline electrolysers are also used in the production of hydrogen for energy storage. Excess electricity, often from renewable sources, can be used to generate hydrogen, which is then stored and later converted back into electricity when needed.
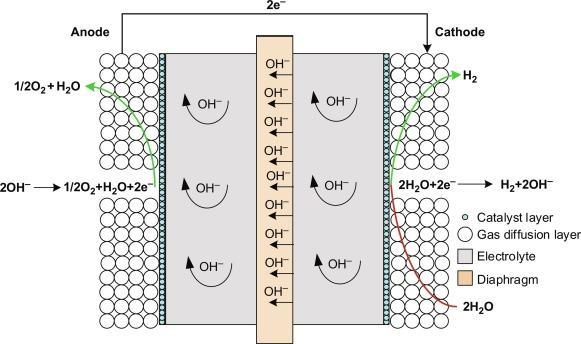
Proton Exchange Membrane (Pem) Electrolysers:
In order to understand different types of electrolysers, PEM electrolysers employ another unique type of electrolyser. In this, hydrogen and oxygen are produced when water electrolysis is conducted through the application of an electrical current to its cell stack. To create H2 on the cathode side, the hydrogen protons cross the membrane.
Also Read: What Is Green Hydrogen Used For As A Fuel For Tomorrow’s World?
Proton Exchange Membrane (Pem) Electrolysers Uses:
1) Green Hydrogen Production:
PEM electrolysers are often used to produce green hydrogen, which is hydrogen produced using electricity from renewable energy sources. This green hydrogen can be used in a wide range of applications, including fuel cell vehicles, industry, and power generation.
2) Portable and Small-Scale Applications:
PEM electrolysers are favored for portable and small-scale applications due to their compact design and fast response time. They are suitable for applications such as backup power systems, off-grid energy solutions, and small-scale hydrogen generation.
3) Fuel Cell Vehicles:
PEM electrolysers are used in the production of hydrogen for fuel cell vehicles. They can provide a source of clean hydrogen to power these vehicles, offering an alternative to internal combustion engines and reducing carbon emissions.
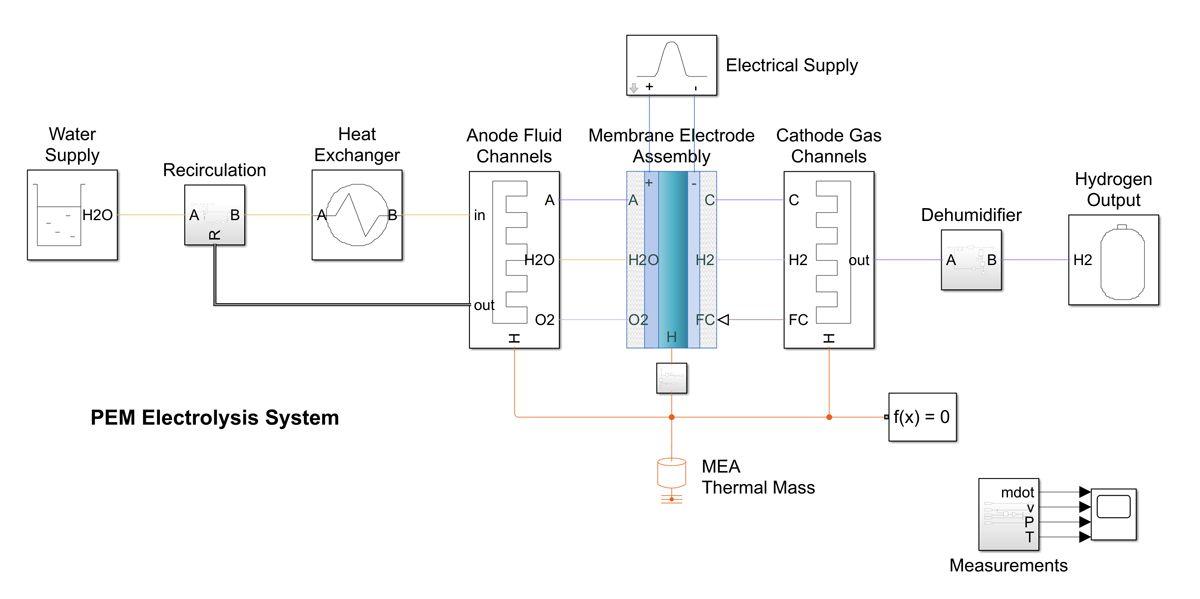
Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell (Soec) Electrolysers:
SOECs differ as they utilize heat to make hydrogen from steam and are best placed where there is a heat source available (nuclear or industrial facilities). They operate at high temperatures (500 – 850 ℃).7 SOECs have shown higher efficiency than other technologies; however, on the flip side, they are not suited to withstand load changes.The technology is still at a demonstration level.
What Are The Uses Of Electrolysers?
Electrolysers are multifunctional instruments mainly employed for the electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen. This hydrogen supports fuel cell cars, energy storage, and industrial processes by acting as a clean energy transporter. They are essential for low-carbon and sustainable solutions in the production of chemicals, water purification, metal extraction, and environmental applications.
Conclusion
Because they provide a sustainable way to produce hydrogen for use as an energy carrier, electrolysers are essential to the clean energy transition. By splitting water into its constituent elements, hydrogen and oxygen, these devices contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future. Based on the needs of the application, the type of electrolyser to use should be selected, taking into consideration variables like size, temperature of operation, reaction time, effectiveness, and hydrogen purity. Electrolysers have the potential to be a key component of the decarbonization of many industries and the further integration of renewable energy sources as technology develops.
FAQ’s:
1) Is An Electrolyser A Fuel Cell?
A fuel cell and an electrolyzer are not the same thing. An electrolyzer is a machine that splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity, producing hydrogen in the process. On the other hand, a fuel cell uses an electrochemical mechanism to mix hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity. Although they both use hydrogen and electrochemical processes, a fuel cell produces electricity, while an electrolyzer produces hydrogen. In essence, a fuel cell uses hydrogen as a fuel source to generate electricity, whereas an electrolyzer generates hydrogen.
2) What Is The Most Common Electrolyser?
The most common electrolysis technology is alkaline based electrolysers.
3) Who Manufactures Electrolyser In India?
There are several companies manufacturing electrolyzers in India, and Avaada Group is indeed one of them. Avaada is developing state-of-the-art Electrolyser manufacturing capacity to cater to the increased demand worldwide. The product is based on a proven technology widely respected for its robustness, reliability, and energy efficiency. Their strategy is to remain ahead of the curve, and with that objective in mind, continuous innovation is a top priority. A dedicated in-house team of scientists and engineers is pursuing research in emerging Electrolyser technologies.